Core Identities and Transaction Identifiers for Blockchains
Etymology: Middle French identité, from Late Latin identitat-, identitas, probably from Latin identidem repeatedly, contraction of idem et idem, literally, same and same (Merriam-Webster Dictionary).
Identity is about trusted data — trusted personal data. Human beings live within social constructs and communities. People who know me can vouch for me. Organizations that know me can issue assertions or attestations about me.
At the heart of all this is the notion of the core identity, something that is inherent as part of me and inalienable from me.
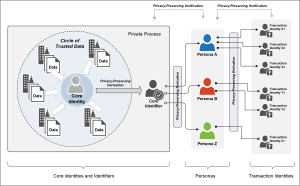
There are a number of key concepts and principles underlying the notion of core identities, core identifiers and personas (see Figure).
A fundamental concept is that of derived identities and derived identifiers which provides not only privacy to its user (the person or organization that it represents) but also a degree of defense in the case of attacks against identity providers (e.g. identity theft) and for a safety net in the rare case of weaknesses within the underlying cryptographic implementations.
I would argue that transaction identities and transaction identifiers are the forms of identities that should be used on the Internet and that they must be derived (e.g. cryptographically) from a core identity which itself must be kept as private or secret. Should a transaction identity be compromised or stolen, it can be placed on a public “blacklist” and a new one be derived for the user. The derivation process or algorithms must maintain the privacy of the user and the secrecy of the user’s core identity.
Some definitions:
We define identity as the collective aspect of the set of characteristic or features by which a thing (e.g. human; device; organization) is recognizable and distinguishable one from another. In the context of a human person, individuality of a person plays an important role in that it allows a community of people to recognize the distinct characteristics of an individual person and consider the person as a persisting entity.
- Core identity: The collective aspect of the set of characteristics (as represented by personal data) by which a person is uniquely recognizable, and from which a unique core identifier may be generated based on the set of relevant personal data.
Thus, for example, the set of transaction data associated with a person can be collated and be used to create a core identity that distinguishes that person from others. Out of this set of transaction data, a core identifier may be generated and be held as a joint secret by its issuer and the person. The core identity pertaining to a person must be kept secret, and not be used in transactions.
- Core Identifier: A secret data (e.g. string) or secret mechanism (e.g. crypto function) that uniquely identifies a person or entity. The core identifier must be immutable, must be kept secret, and never be used directly in transactions.
- Persona: A persona is defined by and created based on a collection of attributes used in a given context or a given relationship. Thus, a person may have a work-persona, home-persona, social-persona, and others. Each of these personas is context-dependent and involves only the relevant subset of the core identity characteristics of that person. A person may have one or more personas.
- Transaction Identity and Identifier: When an individual seeks to perform a transaction (e.g. on the Internet, on a blockchain or other transacting mediums) he or she chooses a relevant persona and derives from that persona a transaction identity (and corresponding digital identifier) to be used in the transaction. A transaction identity maybe short-lived and may even be created only for that single transaction instance. A useful analogy is that of credit card numbers, which may be used at a Point of Sale (POS) locations without the user needing to provide any additional identifiers (i.e. reveal data from their core identity such as Social Security Number) and which may be replaced at any time without impacting the user’s core identity.